Description
Given a nested list of integers, return the sum of all integers in the list weighted by their depth.
Each element is either an integer, or a list – whose elements may also be integers or other lists.
Different from the previous question where weight is increasing from root to leaf, now the weight is defined from bottom up. i.e., the leaf level integers have weight 1, and the root level integers have the largest weight.
Example 1:
Given the list [[1,1],2,[1,1]], return 8. (four 1’s at depth 1, one 2 at depth 2)
Example 2:
Given the list [1,[4,[6]]], return 17. (one 1 at depth 3, one 4 at depth 2, and one 6 at depth 1; 13 + 42 + 6*1 = 17)
DFS solution
Complexity Analysis
The algorithm takes O(N)O(N) time, where NN is the total number of nested elements in the input list. For example, the list [ [[[[1]]]], 2 ] contains 44 nested lists and 22 nested integers (11 and 22), so N=6N=6.
In terms of space, at most O(D)O(D) recursive calls are placed on the stack, where DD is the maximum level of nesting in the input. For example, D=2D=2 for the input [[1,1],2,[1,1]], and D=3D=3 for the input [1,[4,[6]]].
/**
* // This is the interface that allows for creating nested lists.
* // You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation
* public interface NestedInteger {
* // Constructor initializes an empty nested list.
* public NestedInteger();
*
* // Constructor initializes a single integer.
* public NestedInteger(int value);
*
* // @return true if this NestedInteger holds a single integer, rather than a nested list.
* public boolean isInteger();
*
* // @return the single integer that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a single integer
* // Return null if this NestedInteger holds a nested list
* public Integer getInteger();
*
* // Set this NestedInteger to hold a single integer.
* public void setInteger(int value);
*
* // Set this NestedInteger to hold a nested list and adds a nested integer to it.
* public void add(NestedInteger ni);
*
* // @return the nested list that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a nested list
* // Return null if this NestedInteger holds a single integer
* public List<NestedInteger> getList();
* }
*/
public class Solution {
private HashMap<Integer, List<Integer>> hm = new HashMap<>();
private int maxLevel = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
public int depthSumInverse(List<NestedInteger> nestedList) {
int sum = 0;
dfs(nestedList, 1);
for (int level : hm.keySet()) {
// System.out.println("level: " + level);
for (int num : hm.get(level)) {
// System.out.println("num -> " + num);
sum += (num * (maxLevel-level+1));
}
}
return sum;
}
private void dfs(List<NestedInteger> nestedList, int level) {
if (nestedList == null) return;
maxLevel = Math.max(maxLevel, level);
if (!hm.containsKey(level)) {
hm.put(level, new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
for (NestedInteger ni : nestedList) {
if (ni.isInteger()) {
hm.get(level).add(ni.getInteger());
} else {
dfs(ni.getList(), level+1);
}
}
}
}
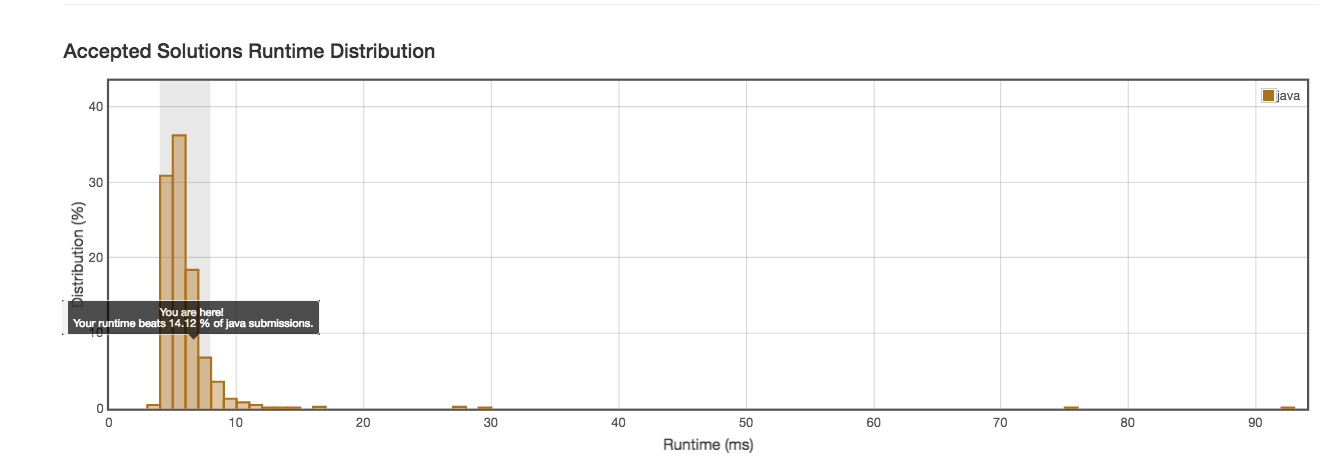 Runtime: 6ms
Runtime: 6ms