Description
Given a binary tree, find the length of the longest consecutive sequence path.
The path refers to any sequence of nodes from some starting node to any node in the tree along the parent-child connections. The longest consecutive path need to be from parent to child (cannot be the reverse).
Note: the description is vague, visit here for explaination link
For example,
1
\
3
/ \
2 4
\
5
Longest consecutive sequence path is 3-4-5, so return 3.
2
\
3
/
2
/
1
Longest consecutive sequence path is 2-3,not3-2-1, so return 2.
O(n) Bottom-up Post-order DFS in Java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
int ret = 0;
/**
* @solution: Post-order DFS
* @runtime: 3ms
*
*/
public int longestConsecutive(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return ret;
}
private int dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int leftSum = dfs(root.left);
int rightSum = dfs(root.right);
if (root.left != null && root.left.val != root.val+1) {
leftSum = 0;
}
if (root.right != null && root.right.val != root.val+1) {
rightSum = 0;
}
ret = Math.max(ret, Math.max(leftSum, rightSum)+1);
return Math.max(leftSum, rightSum)+1;
}
}
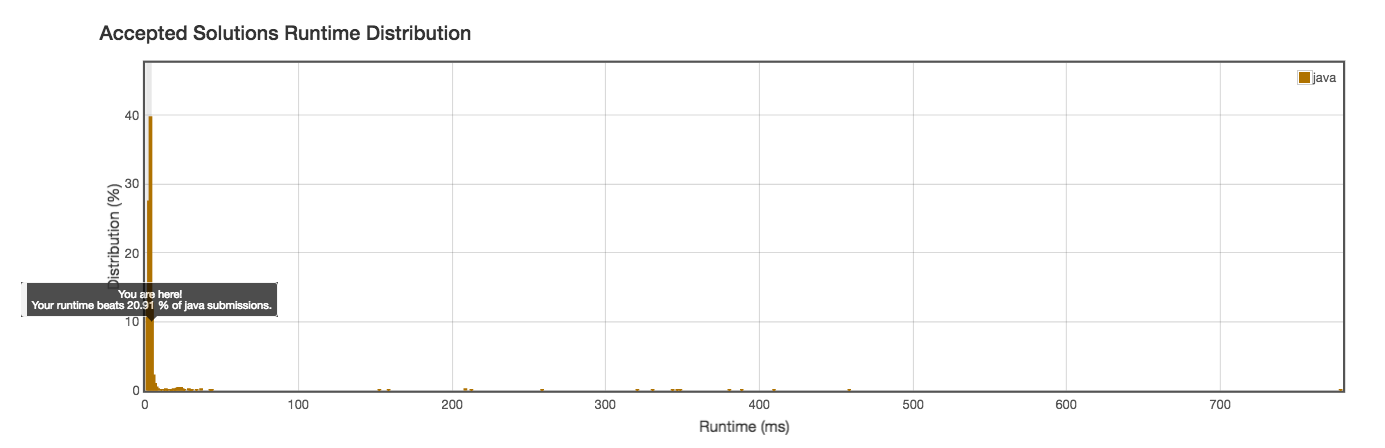 Runtime: 3ms
Runtime: 3ms
O(n) Top-up Pre-order DFS in Python
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def __init__(self):
self.ret = 0
def longestConsecutive(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: int
:algorithm: Pre-order DFS, O(n)
:runtimr: 188ms
"""
if not root:
return 0
self.dfs(root, 1)
return self.ret
def dfs(self, root, carry):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: void
"""
self.ret = max(self.ret, carry)
if root.left:
if root.left.val - 1 == root.val:
self.dfs(root.left, carry+1)
else:
self.dfs(root.left, 1)
if root.right:
if root.right.val - 1 == root.val:
self.dfs(root.right, carry+1)
else:
self.dfs(root.right, 1)
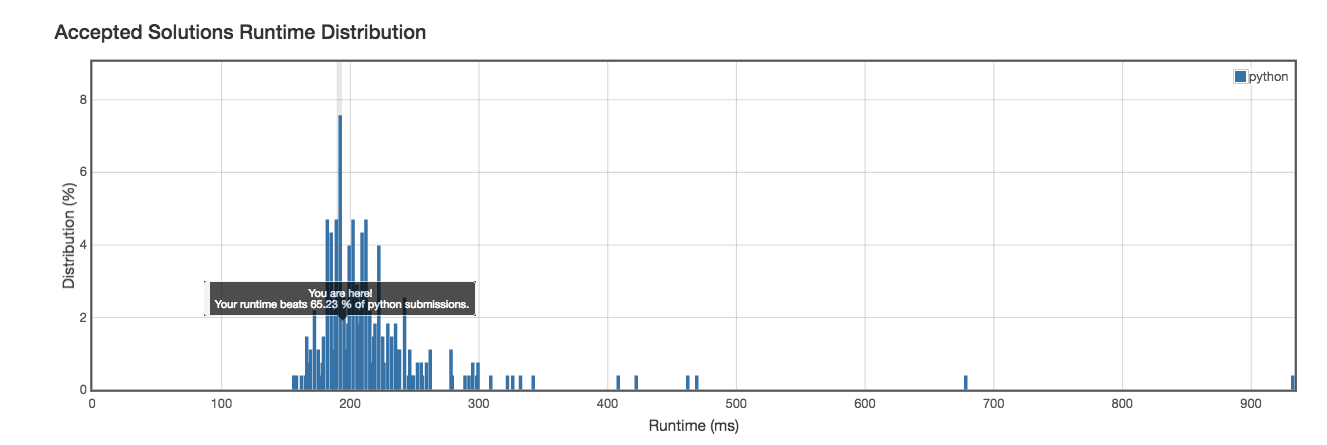 Runtime: 188ms
Runtime: 188ms