Description,
You need to find the largest value in each row of a binary tree.
The leetcode link
Example,
Input:
1
/ \
3 2
/ \ \
5 3 9
Output: [1, 3, 9]
BFS implemted in Java
Natually, the level order BFS is the most straight forward way to tackle this problem – traverse the tree level by level, and find the node with largest value.
Time complexity: O(n)
RUntime: 10ms
Note:
The Queue and Deque both work in BFS. The implementations of Queue/Deque have pros & cons, but in this specific problem, they perform almost the same.
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* Returns a list of ints, which are the largest in their respective levels.
* @param TreeNode the root node of the given tree.
* @return List<Integer> list of integer
*/
public List<Integer> largestValues(TreeNode root) {
Deque<TreeNode> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
List<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return ret;
deque.add(root);
int queueSize = deque.size();
while (queueSize != 0){
int localMax = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < queueSize; i++){
TreeNode node = deque.poll();
localMax = Math.max(localMax, node.val);
if (node.left != null) deque.add(node.left);
if (node.right != null) deque.add(node.right);
}
ret.add(localMax);
queueSize = deque.size();
}
return ret;
}
}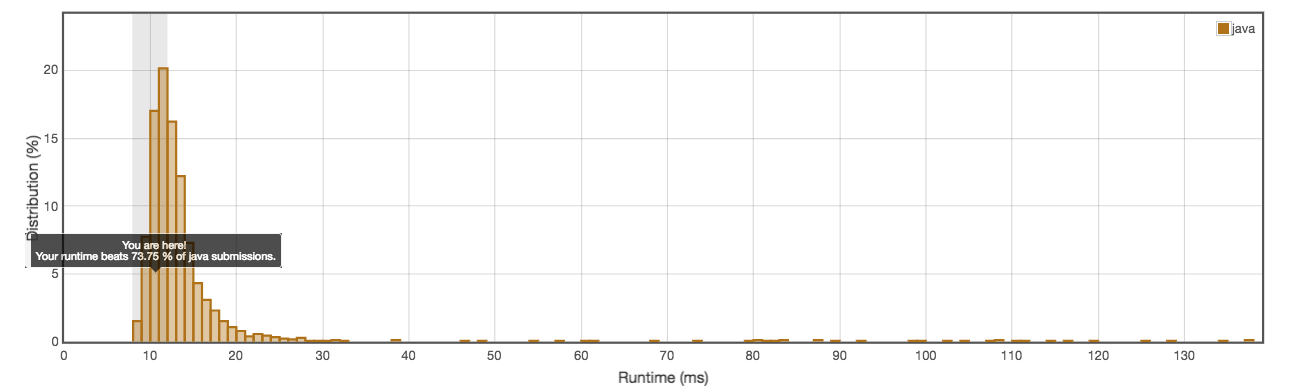 Runtime: 10ms
Runtime: 10ms
Pre-order DFS in Python
This problem could also be solved by pre-order DFS.
Create an empty bucket, whenever traversing to a new level, increase bucket size by 1.
When reaching a level already exists in the bucket, compare the existing value with the current node’s vaue. Update the bucket value to the larger one.
Because this is an one-pass traversal, the time complexity is O(n), where n is the tree node count.
Time complexity: O(n)
Runtime: 68 ms
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def largestValues(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: List[int]
"""
ret = []
self.dfs(root, ret, 0)
return ret
def dfs(self, root, ret, level):
"""
@param: TreeNode, List<int>, int
@return: void
"""
if not root:
return
if level == len(ret): # when first time reaching a new level
ret.append(root.val)
else:
ret[level] = max(ret[level], root.val)
self.dfs(root.left, ret, level+1)
self.dfs(root.right, ret, level+1)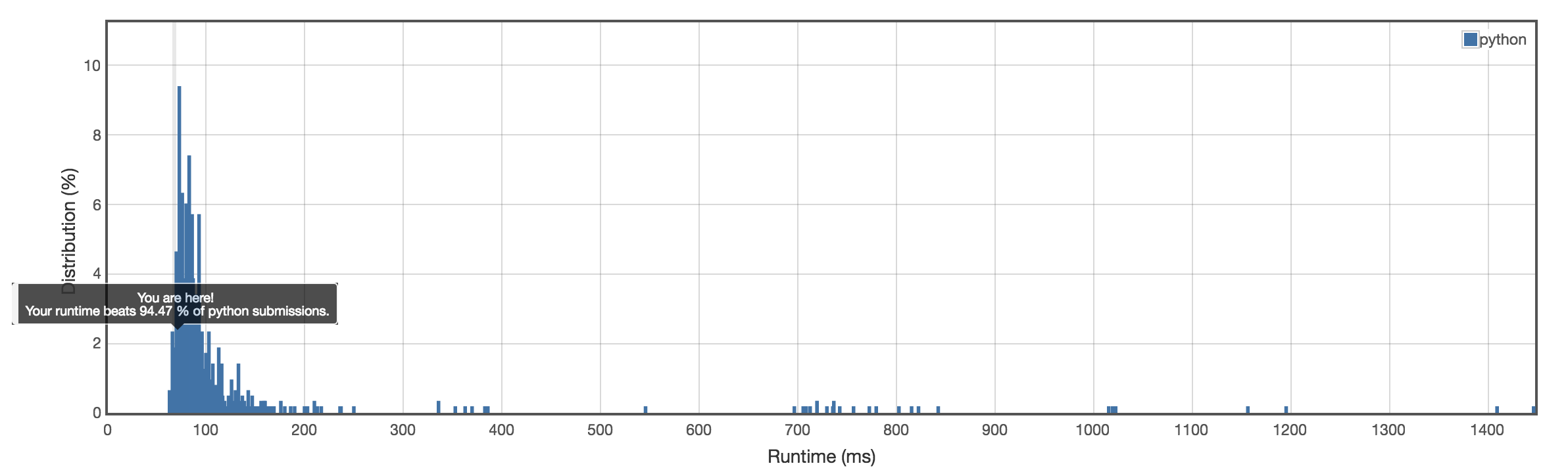 Runtime: 68ms
Runtime: 68ms