Description,
Given a binary tree, return all root-to-leaf paths.
For example, given the following binary tree:
1
/ \
2 3
\
5
All root-to-leaf paths are:
[“1->2->5”, “1->3”]
Pre-order DFS with backtracing
This version of solution uses backtracing. Alternatively, you can pass a string as argument at recurssion, instead of backtracing a list, which is faster because you avoid the cost of list’s append / pop operations.
Time complexity: O(n)
Runtime: 7ms
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* Backtracing solution
* DFS, O(n)
* Runtime: 18ms, top 45%
*/
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
List<String> ret = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(root, ret, path);
return ret;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, List<String> ret, List<Integer> path){
if (root == null) return;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
path.add(root.val);
ret.add(listToString(path));
path.remove(path.size()-1);
return;
}
path.add(root.val);
dfs(root.left, ret, path);
dfs(root.right, ret, path);
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
/**
* Init a StringBuild outside of the loop is the
* most efficient way of concatenate strings.
*/
private String listToString(List<Integer> path) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
String prefix = ""; // otherwise, alternative is to use sb.setLength(sb.size()-1);
for (int i : path) {
sb.append(prefix);
prefix = "->";
sb.append(i);
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
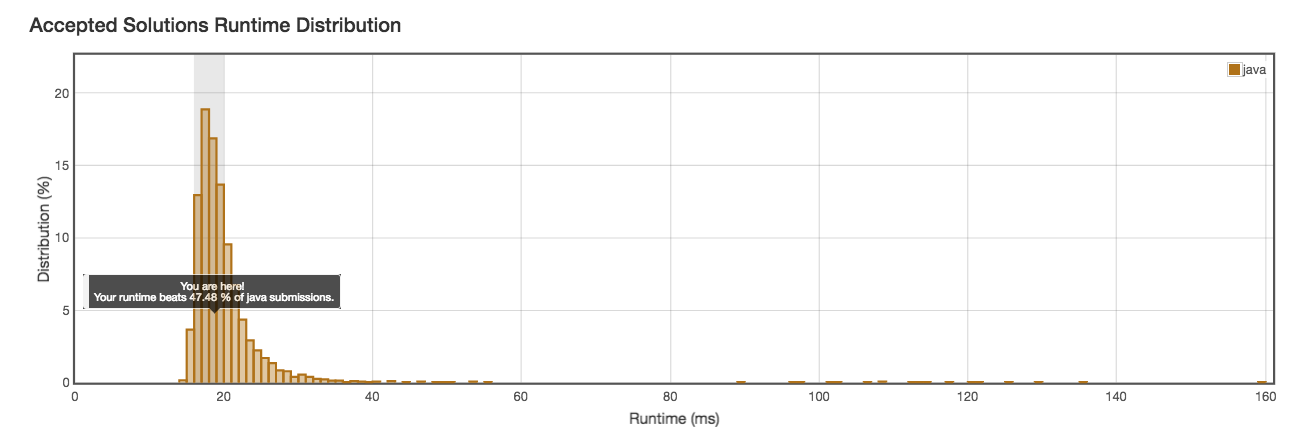 Runtime: 18ms
Runtime: 18ms
Python version
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
# @param {TreeNode} root
# @return {string[]}
# @runtime: 49ms, 50%
def binaryTreePaths(self, root):
if not root:
return []
res, path = [], []
self.dfs(root, path, res)
return res
def dfs(self, node, path, res):
if not node:
return
if not node.left and not node.right:
path.append(node.val)
res.append("->".join(map(str, path)))
path.pop()
return
path.append(node.val)
self.dfs(node.left, path, res)
self.dfs(node.right, path, res)
path.pop()
"""DFS
def binaryTreePaths(self, root):
if not root:
return []
res = []
stack = []
stack.append((root, []))
while stack:
node, path = stack.pop()
if not node.left and not node.right:
path += [node.val]
res.append("->".join(map(str, path)))
if node.right:
stack.append((node.right, path+[node.val]))
if node.left:
stack.append((node.left, path+[node.val]))
return res
"""
"""BFS
from collections import deque
def binaryTreePaths(self, root):
if not root:
return []
res = []
dq = deque()
dq.append((root, []))
while dq:
node, path = dq.popleft()
if not node.left and not node.right:
path += [node.val]
res.append("->".join(map(str, path)))
if node.left:
dq.append((node.left, path+[node.val]))
if node.right:
dq.append((node.right, path+[node.val]))
return res
"""